Medicine for Cancer Patients: Latest Advances and Breakthrough Treatments
Cancer is considered one of today’s biggest and hardest health problems, affecting a large number of people around the world. More effective treatments and therapies are being introduced every year for people living with cancer. The search for effective medicine for cancer patients has taken a significant leap forward thanks to cutting-edge research, personalized medicine, and advancements in biotechnology. Now, we have cancer treatments that are aimed at the tumor, use less toxic chemicals and work better than in the past.
Learning about How Cancer Medicine Has Changed
In the past, the main methods for treating cancer were surgery, radiation therapy and conventional chemotherapy. These methods are popular now but are usually associated with many unwelcome side effects. For the past two decades, the industry has worked to produce more precise cancer drugs. These new approaches are designed to kill cancer cells and also protect your healthy tissues, reduce the likelihood of side effects and improve your living conditions.
A new set of drugs has been introduced recently which use immunotherapy, targeted therapy and genes. They provide a move from general cancer care to care that fits each person’s genetics, as treatment is adapted based on the information in the patient’s and tumor’s genes.
Learning has continued in the field of Targeted Therapy.
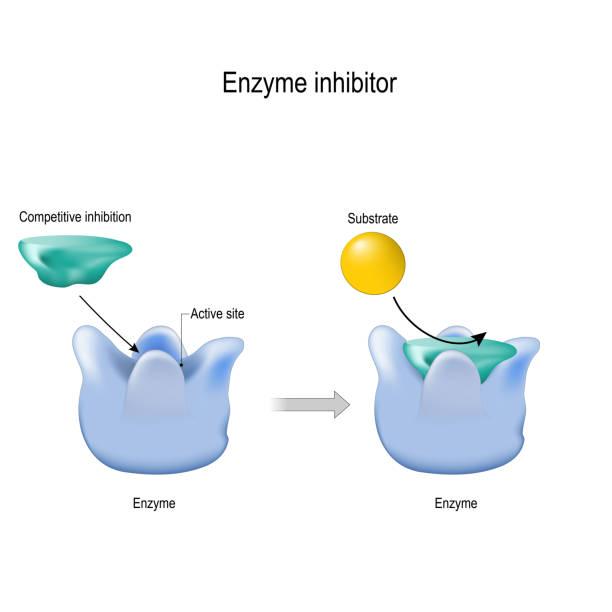
One of the most significant advancements in medicine for cancer patients is the rise of targeted therapy. Unlike chemotherapy which targets lots of growing cells, targeted drugs aim at changes in cancer cells that cause them to grow. Such medicines go after certain markers found on cancer cells which increases their effectiveness and keeps less harm to the body.
Both trastuzumab used in treating HER2-positive breast cancer and osimertinib for selected cases of lung cancer have demonstrated excellent results. They have the effect of switching off chemical messengers needed for cancer cells to thrive which allows doctors to control or stop tumor growth. Because targeted treatments have succeeded, researchers are still looking for biomarkers related to various cancer types.
Using Immunotherapy to Help the Body Fight Diseases
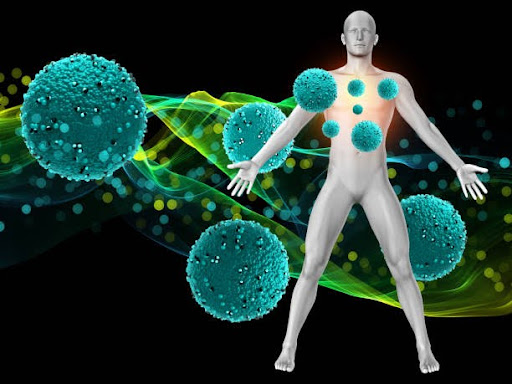
Because of immunotherapy, our approach to treating cancer has been greatly changed. Rather than targeting cancer cells directly, immunotherapy makes the patient’s immune system notice and fight cancer. Many cancer treatments have benefited a great deal from this approach.
Treatments with pembrolizumab and nivolumab have been successful in controlling melanoma, lung cancer and other types of cancer. Immunotherapy works by stopping proteins that stop immune cells fighting against cancer, freeing the immune system to fight. In turn, our bodies have stronger ways to fight against tumor growth.
For certain patients, having immunotherapy has allowed them to maintain remission even when cancer is advanced. Investigators are examining if using combinations of immunotherapy with other approaches increases how well the therapy works.
Personalized and Precision Medicine Are Being Developed
Oncology is being changed by the rise of precision medicine. With a patient’s genetics and that of their tumor in hand, doctors can choose treatments that are troublesome and effective. This personalized approach is revolutionizing the use of medicine for cancer patients, offering new possibilities for individualized care.
Genomic testing allows oncologists to detect changes in cancer cells that affect the disease. Afterward, drugs are created or chosen to focus on those specific deviations. Because of this, new therapies are now available for cancers that were previous hard to treat, including leukemias, ovarian cancers and pancreatic cancers.
It is now possible to use blood tests, known as liquid biopsies, to track the success of a treatment and notice if cancer comes back. Such advancements are major factors in moving cancer treatment to strategies that respond better to patients.
New advances in Hormonal and Biological Therapies

When treating hormone-sensitive cancers such as breast and prostate, doctors rely on hormonal therapy. They prevent the body from making or using hormones that help cancer grow. Tamoxifen, aromatase inhibitors and enzalutamide have all been shown to help treat prostate cancer when given alone or together with different treatments.
Biological therapies, including monoclonal antibodies, are another important class of medicine for cancer patients. Such agents attach themselves to chosen parts of the cancer cells and make these cells easier for the immune system to find and destroy. They frequently deliver toxic agents to cancer cells which helps make the treatment more accurate.
Cancer vaccines and mRNA technology go hand in hand.
Since mRNA vaccines have worked so well against COVID-19, scientists are exploring their use against cancer. Scientists are developing cancer vaccines that can be used to help the immune system attack cancer cells related to the markers on each patient’s cancer. The discipline offers the chance to develop individual medications that could help keep cancer from returning.
Some mRNA cancer vaccines are now being tested in people who have melanoma, pancreatic cancer or glioblastoma. If successful, these could become a new frontier in medicine for cancer patients, offering innovative options beyond conventional therapies.
STI treatment is improved when more than one therapy is used.
It is common now for doctors to use different therapies at the same time to improve how cancer patients respond. Chemotherapy when combined with immunotherapy or even radiation combined with a biological agent, are emerging as promising ways to treat cancer.
Having different types of medicines together helps fight cancer so resistance is less likely and the chance of a cure improves. These drugs also need to be well coordinated and overseen to help stop the risk of some toxicities from being too strong.
Making services easier to use and less costly
Despite these promising advances, access to advanced medicine for cancer patients remains a concern. Because prices for medicines are high, not all patients have access to medical treatments when needed. Currently, both governments, NGOs and pharmaceutical companies are trying to make advanced treatments accessible worldwide.
Because of biosimilars that work like expensive biologic drugs, having another option that is less expensive is becoming more frequent. Also, various groups worldwide are making sure that clinical trials encourage diversity, increasing the chances that new treatments will help more people.
Hope Continues to Grow
Cancer is often not the automatic result in death that it was in the past. With the rapid pace of scientific advancement, medicine for cancer patients is evolving toward more personalized, effective, and compassionate care. More powerful than ever, cancer can now be attacked using targeted therapy, immunotherapy, gene-based treatments and vaccines.
Such developments give patients and their families more than new medicine; they see them as signs of coming changes such as more time, better health and perhaps, a cure. As new findings and tools are developed, it looks like cancer medicine is heading in a very positive direction.
Conclusion
There are more advancements now in oncology than ever before. Every time new knowledge is gained, our methods for treating cancer become more accurate and effective. Whether through targeted therapies, immunotherapies, or personalized medicine, the latest medicine for cancer patients offers a future filled with optimism. Keeping up to date with these advances is key for all—patients, caregivers and healthcare professionals—to help make cancer our ally in the future.